An introduction to Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Jon Spriggs (He/Him)
What is MFA?
* Previously known as “Second Factor” or “Two Factor” authentication
Type: Incrementing Counters
SMS MFA
Generated on a server, this message could just have easily read “Security Code: 000000” for all that the cryptography isn’t verifiable anywhere. Also, this message could be re-routed or inspected using SS7 – the signalling system used by all international telecoms companies, or the telco could give your phone number to someone else – often seen in Cryptocurrency attacks, known as SIM swapping.
So, what else are your options?
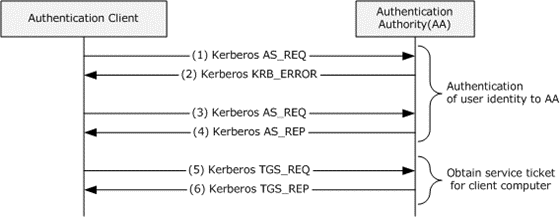
RSA SecurID
Citation ]
Now – 2
Now – 1
Now
Now + 1
Now + 2
942870
070618
140504
890059
692790
* Requires RSA Authentication ServerHow does it work?
* “Maths” with seed plus internal clock = code
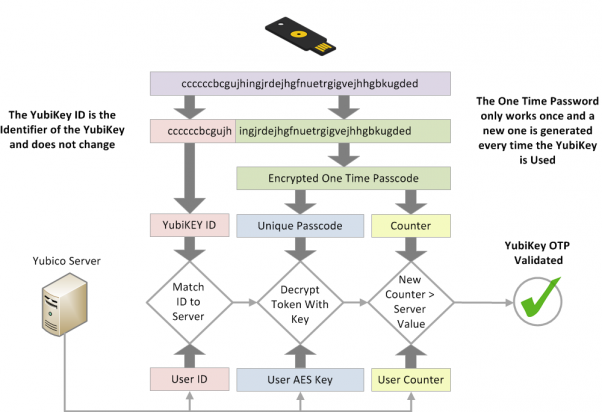
HMAC-based One Time Passcode (HOTP)
OATH in 2005 as RFC4226
* Rather than relying on a clock, HOTP just uses a counter and the seed key.
How does it work?
* “Simple” maths HOTP(K,C) = Truncate(HMAC-SHA-1(K,C))where “K” is the key, and “C” is the counter.
Time-based One Time Passcode (TOTP)
OATH in 2011 as RFC6238, most commonly referred to as “Google Authenticator” codes.
* Based on HOTP, but again, replacing the counter with the “epoch” time (seconds since 1970-01-01 00:00:00) in 30 second increments. TOTP = HOTP(K, int(epoch/30))citation ]
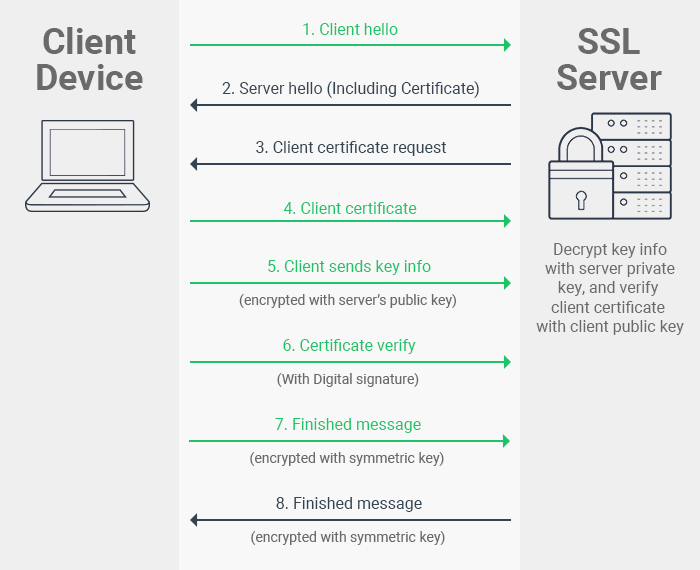
Client Certificates
Comodo )Microsoft )
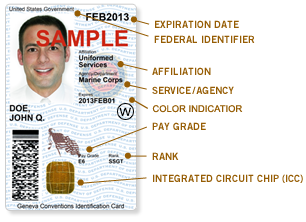
Personal Identity Verification (PIV) Smartcards
FIPS 201 .
These hold an X.509 Private Key, which is signed by a centrally managed Certificate Authority. Most commonly issued in the US by the DOD, in the UK by the NHS authorities.
EMV Smartcards
Wikipedia )
EMV Cards can cryptographically sign requests, and the CAP program uses this feature to provide confirmation of a “cancellation of a transaction” that would typically be used in a payment terminal but that doesn’t require access to the network.
These transactions are either:
1. Sign: provided with the EMV PIN, a challenge code and amount (e.g. “1234 5678” and “100.00”) typically used to approve a transaction.
Each of these modes actually uses the PIN, challenge code and amount, where the later modes (respond and identify) provide all zeros for the missing fields (challenge code and/or amount).
Hardware Tokens
Other vendors are available
U2F and WebAuthn
With both U2F and WebAuthn, the browser (via a Javascript API) can communicate with the authentication platform (the token) and ask that to sign a request.
“Signing a request” is achieved by pressing the physical button on a USB or Bluetooth attached device, or by tapping an NFC device to the client machine.
These are not always feasible with mobile devices, where resorting to other systems providing the MFA may be preferable.
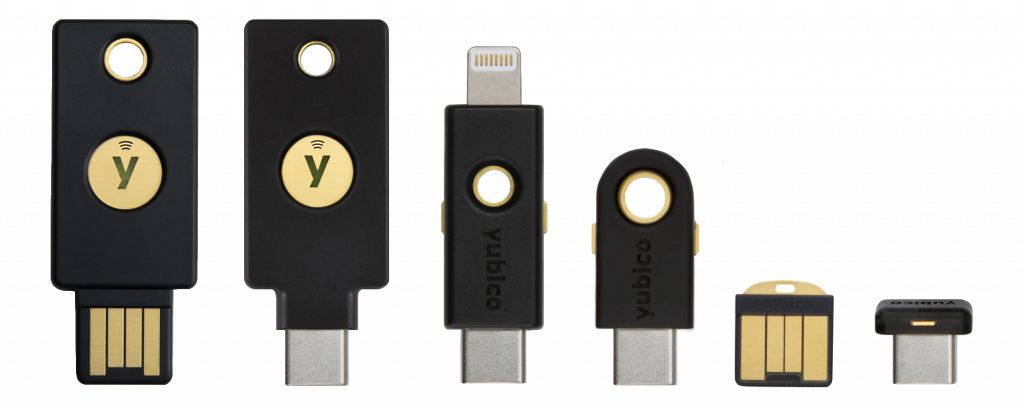
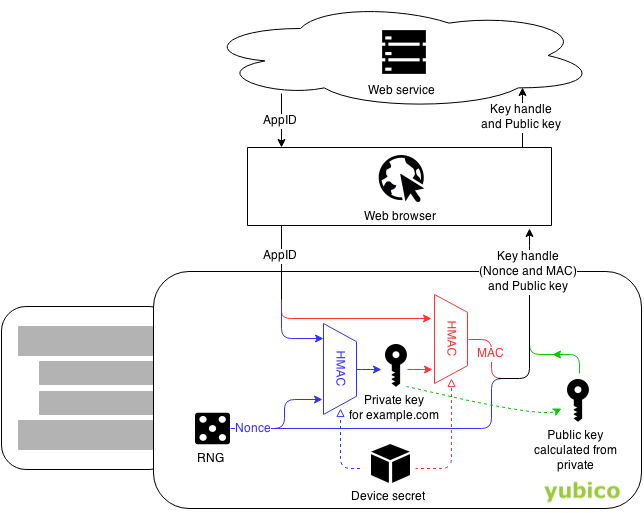
Yubico OTP
Yubico )Bless you
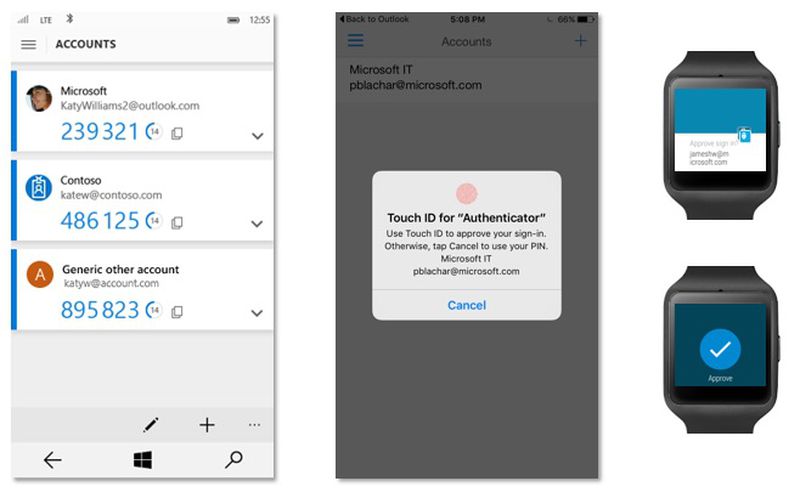
Application Based
Between Microsoft’s Authenticator, and Android’s “Sign in with your phone”, if you have a pre-existing authentication with a service on a device, you might find it easier to sign in using that application. These work by sending a push notification to your device over the existing HTTP application channel to request approval. Beware, however, that you should also have an additional MFA method (e.g. hardware token, TOTP or similar) for when your phone doesn’t work, and if someone manages to log into another device, they’ll be able to sign in with that device.
What do I use?
A combination of nearly all of these! I prefer TOTP, as my password safe stores these for me, but I have a personal Yubikey, I used to manage an RSA SecurID Server, my bank likes EMV CAP, I use my phone to approve sign-ins to my Google account and I’ll often get the SMS based authenticators… And wherever possible, I will…
Thanks!
Jon Spriggs (He/Him)
https://jon.sprig.gs
![]()